System Operations
Energy context and nuclear power
Research institutions, nuclear technology developers, vendors and utilities are interested in transforming how nuclear energy meets ever-growing energy demand. Traditionally, nuclear energy has been used to generate electricity — currently providing around 20% of electricity used in the U.S. However, its role is evolving. Nuclear energy use can be further enhanced by optimizing energy use through novel systems integration and process design — leveraging this highly reliable, dispatchable and concentrated energy source.
The primary output from a nuclear fission reactor is heat. Using it for nonelectrical energy services and products in addition to generating electricity will help establish energy abundance for the growth of the industrial and transportation sectors. These integrated or hybrid applications overcome the technical and economic barriers that inhibit the wider use of nuclear energy.
Role of IES
IES’s include coordinated and tightly coupled energy system designs. In a coordinated system, multiple generators may interact within a grid involving loosely coupled electrical, thermal and chemical networks plus various scales of energy storage to provide reliable, sustainable and affordable energy to a variety of energy users.
A tightly coupled system involves co-design and co-control of multiple generators and users integrated via thermal, electrical and chemical means, potentially including various forms of energy storage to provide low-cost electricity and support the production of other commodities.
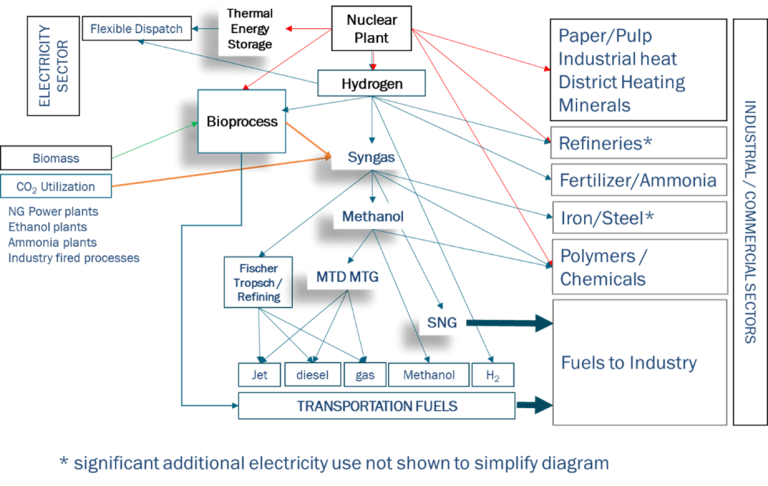
Goals of the IES program
The IES program focuses on the conversion of nuclear-generated energy into energy intermediates and products. This includes, for example, gases, minerals, refined metals, chemicals/chemical feedstocks, fuels and freshwater. This focus is reflected in the energy flows in the following figure.
As advanced reactor technologies come into the marketplace (e.g., high-temperature reactors), more opportunities will arise for integrating these innovative energy systems into new or existing industrial infrastructure. The IES program will accelerate the integration of nuclear and thermal energy sources with industry to provide enduring energy abundance to support U.S. manufacturing and fuels production.
IES demonstrations
The DOE-NE Light Water Reactor Sustainability Program’s Flexible Plant Operations and Generation Pathway manages demonstrations related to the fleet of light water reactors. In 2021, the IES program partnered with the National Reactor Innovation Center to design an advanced reactor IES test bed for demonstrations (see the center’s April 2021 Integrated Energy Systems Demonstration Pre-Conceptual Designs report for more information).
The evolution of the electrical grid and a domestic and global trend to enhance adoption of advanced energy generation and use across all energy sectors will require more coordination of energy generation sources across traditionally independent energy use sectors.